In optically transparent media, a convenient alternative to direct field measurement by acoustic receivers is the optical visualization method. It allows qualitative, and in some modifications even quantitative, studying of the spatial structure of the ultrasonic field in real time.
The shadow method is widely used in shock wave physics. The key figures in its development were such outstanding scientists as:
- Hooke, who was the first to conduct the first direct observation of a temperature disturbance against the background of a distant “light-shadow” boundary;
- Foucault, who proposed using the shadow method to test the shape of mirrors to block the unrefracted light with a special diaphragm – the “Foucault knife“;
- Toepler, who developed an experimental system for observing optical inhomogeneities using the “dark field method” (schlieren method).
An important contribution to the practice of using the schlieren method was made by Mach, who received, in particular, the first shadow image of a shock wave from an electric spark.
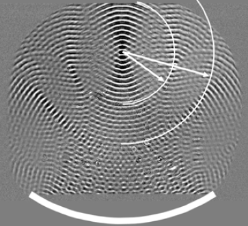
The essence of the schlieren method
- A beam of light rays from a point or slit source is directed by a lens or a system of lenses and mirrors to the studied area of optical inhomogeneity and, after passing the specified area, is focused on an opaque sharp edge (Foucault knife), so that the image of the source is projected onto the very edge of the knife.
- If the studied area is optically homogeneous, then all rays are retained by the knife
- In the presence of inhomogeneities, the light rays undergo refraction and some of them, having deflected, pass by the knife. By placing a lens behind the knife, these beams can be projected onto a screen or a sensitive camera matrix and an image of the inhomogeneities can be obtained.
The above-mentioned fundamental approach has many modifications applicable to different areas of research.
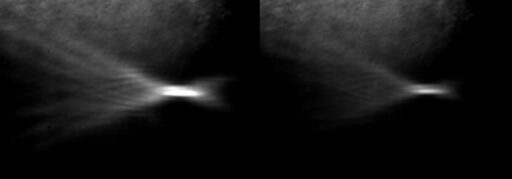
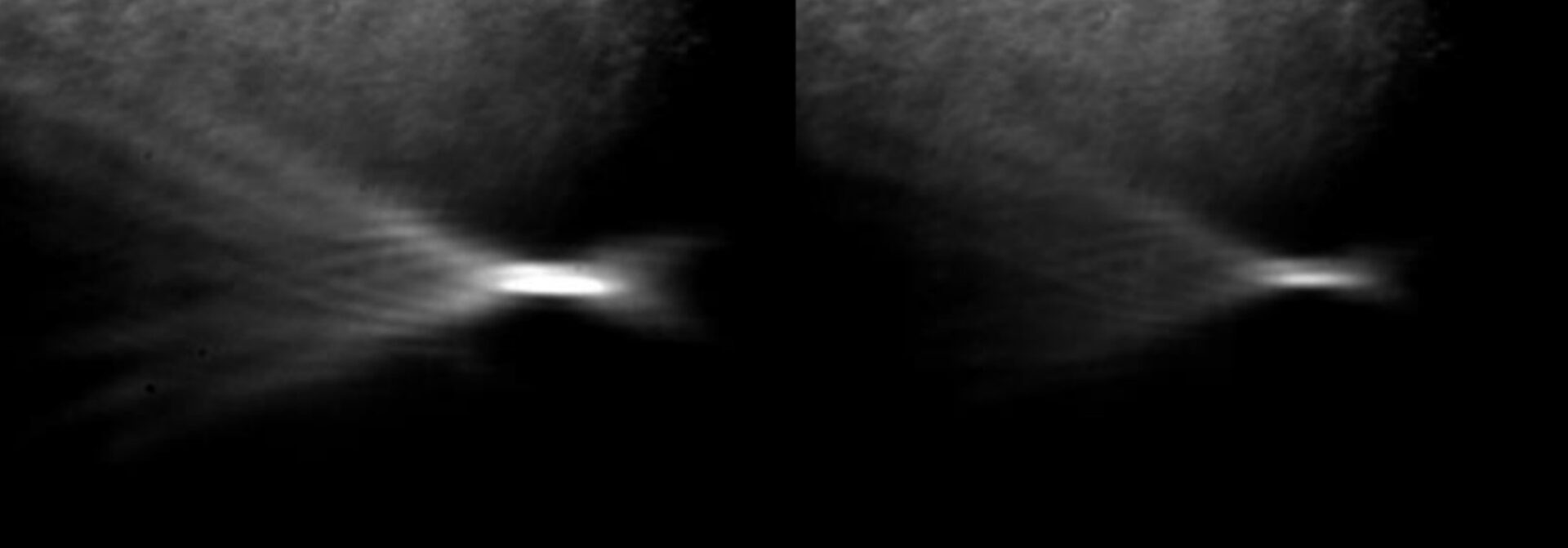
Pulsed shadow pattern of caustics formed in water when ultrasound is emitted by a concave piezoelectric plate
A compact experimental setup based on off-axis parabolic mirrors has been developed at the LIMU Laboratory, which allows the use of the schlieren method for visualizing ultrasonic fields in water. It was used to study the features of the spatial structure of acoustic fields and wave effects that arise during the propagation of ultrasound from pulsed diagnostic probes and powerful sources that generate nonlinear fields.
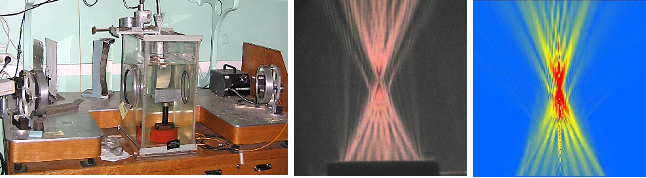
Activity types
- experiment
- numerical modeling
Contacts
[1] Finding the dispersion relations for lamb-type waves in a concave piezoelectric plate by optical visualization of the ultrasound field radiated into a fluid / O. A. Sapozhnikov, M. A. Smagin // Acoustical Physics. — 2015. — Vol. 61, no. 2. — P. 181–187. DOI: 10.1134/S106377101501011X
[2] Шлирен-система для исследования структуры ультразвуковых полей в жидкости / А. И. Цеханович, С. А. Петросян, С. А. Цысарь, О. А. Сапожников // Ученые записки физического факультета Московского Университета. — 2020. — № 5.