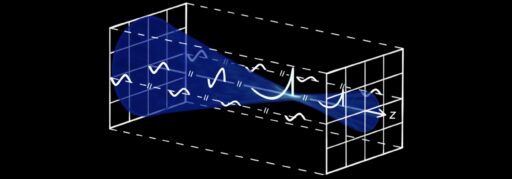
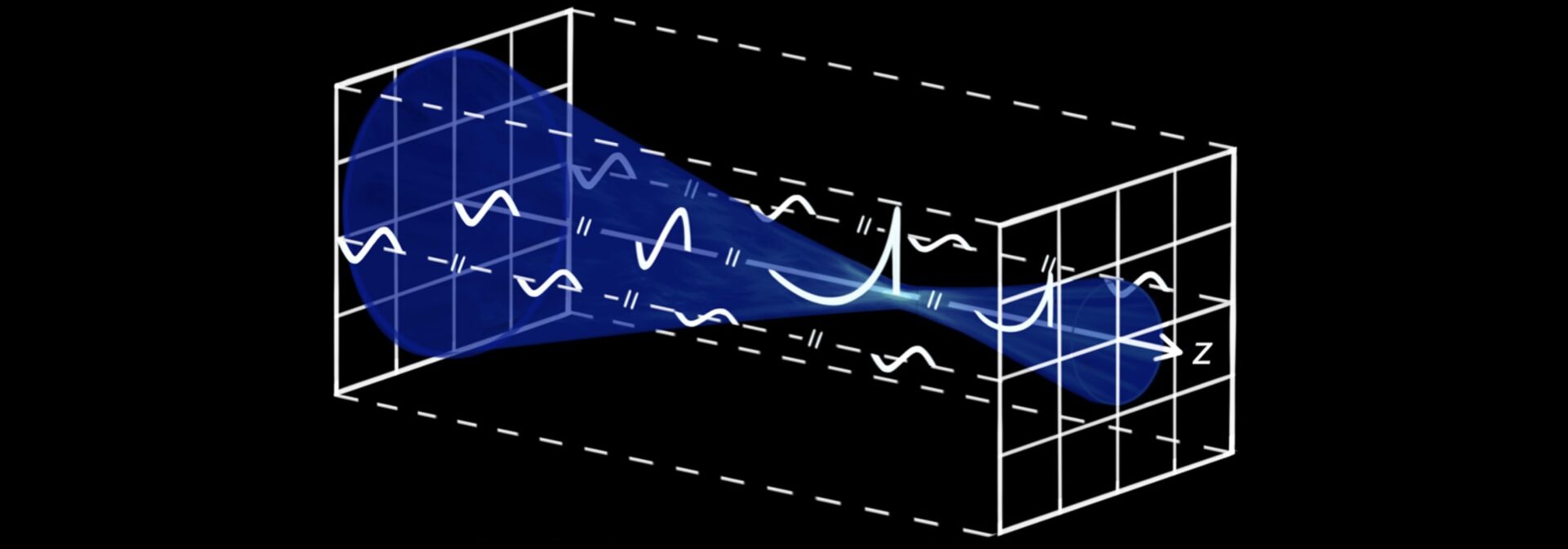
Numerical experiments are increasingly used to develop ultrasonic transducers and characterize the fields they generate.
Numerical modeling of nonlinear ultrasonic fields using central processing units (CPUs) can take up to several days, even after simplifying the task and organizing calculations on several CPU cores.
Parallel programming on graphic processing units (GPUs), which have several thousand highly specialized cores, significantly speeds up calculations and makes it possible to carry them out on personal computers.
LIMU tasks
- Optimization of acoustic field calculations using parallel computing on GPU
- Implementation of various numerical schemes for modeling fields generated by transducers of varied geometry
Activity types
- numerical modeling
Contacts
Details
[1] The use of graphic accelerators in simulation of nonlinear ultrasonic beams with shock fronts on the basis of the westerwelt equation / E.O. Konnova, V.A. Khokhlova, P.V. Yuldashev. // Acoustical Physics. — 2022. — Vol. 68, no. 6. — P. 529–536. DOI: 10.1134/S1063771022060161
[2] Comparative characterization of nonlinear ultrasound fields generated by Sonalleve V1 and V2 MR-HIFU systems / M. M. Karzova, W. Kreider, A. Partanen et al. // IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control. — 2023. — Vol. 70, no. 6. — P. 521–537. DOI: 10.1109/TUFFC.2023.3261420
[3] Performance and accuracy analysis of nonlinear k-Wave simulations using local domain decomposition with an 8-GPU server / B. Treeby, F. Vaverka, J. Jaros // Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. / 2018. — Vol. 34. — P. 022002. DOI: 10.1121/2.0000883